Collision of River Otters#
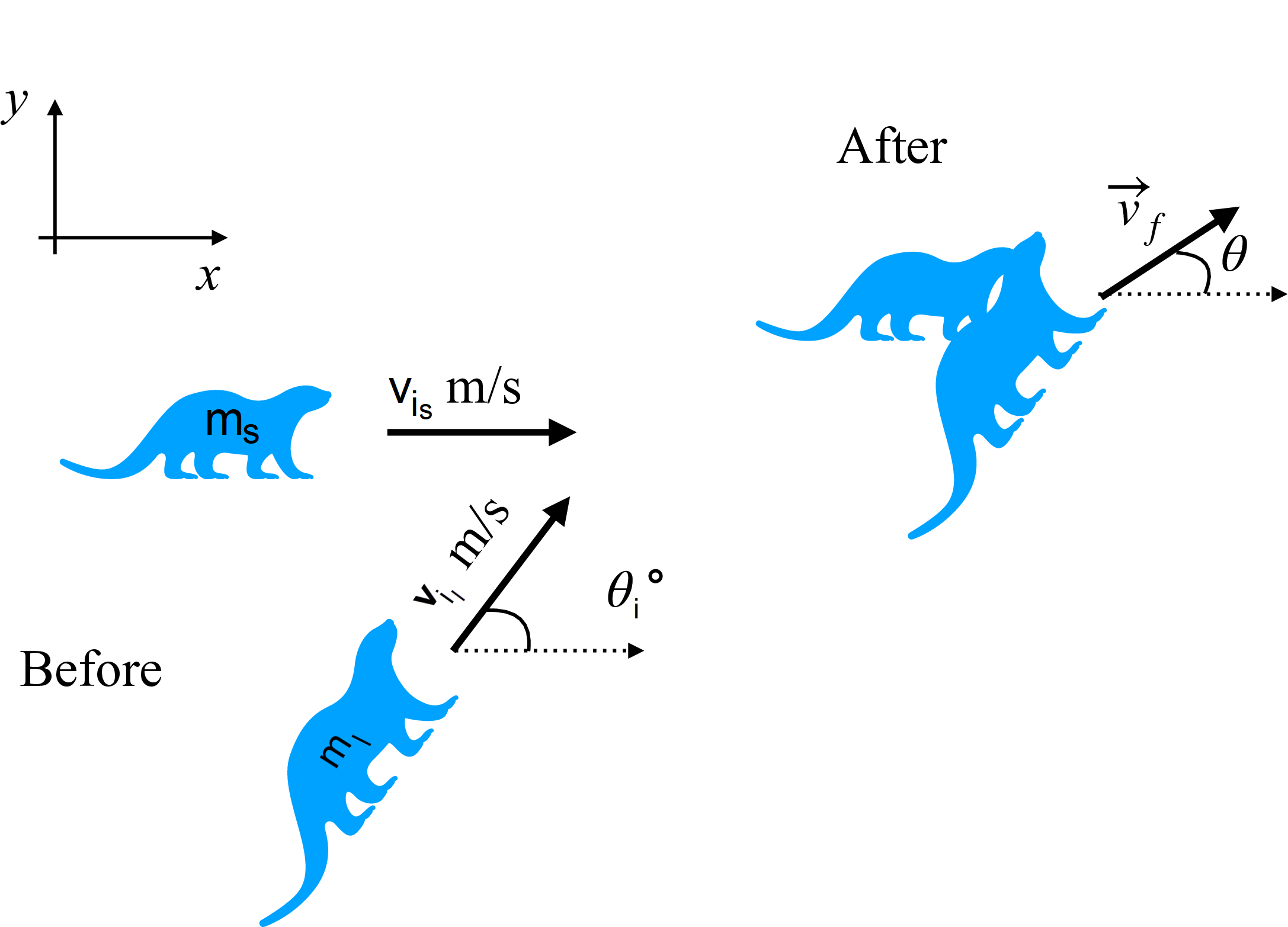
Two river otters collide while sliding across frictionless ice and get tangled together following the (perfectly inelastic) collision as shown in the figure, where a coordinate system has been defined.
The smaller otter (\(m_s =\) 4.83 \(kg\)) is initially moving at \(v\_{i_s} = \) 4.51 \(m/s\) along the x-axis, while the larger otter (\(m_l =\) 9.27 \(kg\)) is initially moving at \(v\_{i_l} = \) 6.71 \(m/s\), \(\theta_i=\)48.8\(^{\circ}\) counterclockwise from the x-axis.
Part 1#
Find the \(x\)-component of the initial momentum of the smaller otter.
Answer Section#
Please enter in a numeric value in \(kg\cdot m/s\).
Part 2#
Find the \(y\)-component of the initial momentum of the smaller otter.
Answer Section#
Please enter in a numeric value in \(kg\cdot m/s\).
Part 3#
Find the \(x\)-component of the initial momentum of the larger otter.
Answer Section#
Please enter in a numeric value in \(kg\cdot m/s\).
Part 4#
Find the \(y\)-component of the initial momentum of the larger otter.
Answer Section#
Please enter in a numeric value in \(kg\cdot m/s\).
Part 5#
Find the \(x\)-component of the total final momentum of the tangled otters in component form.
Answer Section#
Please enter in a numeric value in \(kg\cdot m/s\).
Part 6#
Find the \(y\)-component of the total final momentum of the tangled otters in component form.
Answer Section#
Please enter in a numeric value in \(kg\cdot m/s\).
Part 7#
What direction do the river otters end up heading in, relative to the \(x\)-axis as defined in the figure?
Answer Section#
Please enter in a numeric value in degrees.
Part 8#
What is the speed of the otters after this collision?
Answer Section#
Please enter in a numeric value in \(m/s\).
Part 9#
Is kinetic energy lost, gained, or does it remain constant in this collision?
If the difference in kinetic energy is less than 0.05, consider that kinetic energy has remained unchanged.
Answer Section#
Kinetic energy is lost in this collision.
Kinetic energy is gained in this collision.
Kinetic energy remains constant in this collision.
Attribution#
Problem is licensed under the CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.