Lab 3: Introduction to Python¶
In this lab you will be working on python basics.
This lab must be completed individually.
Where provided, try your best to match the Sample Output as best as you can.
Accept the lab¶
To accept this lab on GitHub Classroom, you must click this link.
Here is a video introduction to Lab 3.
Objectives¶
Practice Python loops and conditions
Practice Python lists and dictionaries
Practice string manipulation in Python
Practice importing and using the Pandas module
Part 1: Python Fundamentals (10 marks)¶
This part of the lab takes you through some of the fundamental components of Python.
1A: if-elif-else statements (2 marks)¶
Fill in missing pieces of the following code such that print statements make sense. You should replace <YOUR_CODE_HERE> with your code.
name = 'Jon Snow'
### Your solution here
if <YOUR_CODE_HERE>:
print('Name "{}" is more than 18 chars long'.format(name))
length_description = 'long'
elif <YOUR_CODE_HERE>:
print('Name "{}" is more than 15 chars long'.format(name))
length_description = 'semi long'
elif <YOUR_CODE_HERE>:
print('Name "{}" is more than 12 chars long'.format(name))
length_description = 'semi long'
elif <YOUR_CODE_HERE>:
print('Name "{}" is 9, 10 or 11 chars long'.format(name))
length_description = 'semi short'
else:
print('Name "{}" is a short name'.format(name))
length_description = 'short'
File "<ipython-input-2-c5380f320f4d>", line 3
if <YOUR_CODE_HERE>:
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
1B: for loops (2 marks)¶
Fill <YOUR_CODE_HERE> in the code snippet below so that this sample output is printed:
Sample Output¶
A
AA
AAA
AAAA
AAAAA
AAAA
AAA
AA
A
### Your solution here
n = 10
for i in range(1,n):
if <YOUR_CODE_HERE>:
print("A" * <YOUR_CODE_HERE>)
else:
print("A" * (<YOUR_CODE_HERE>))
1C: for loops and lists¶
We have given you some sample code, as well as a list called data.
data = [53,9,5,90,63,5,97,40,92,48,53,8,38,63,13,15,66,81,57,79,42,91,25,89,66,4,73,45,80,17]
For each of the exercises 1C1 - 1CX, use the data list to answer the question by writing the appropriate bits of python code.
1C1. Print values that are within the upper and lower bounds of 15 and 40 (2 marks)¶
Hint: Use a for loop and loop through each of the elements in data
Sample output (it’s okay if yours is vertical rather than horizontally printed):¶
[40, 38, 15, 25, 17]
data = [53,9,5,90,63,5,97,40,92,48,53,8,38,63,13,15,66,81,57,79,42,91,25,89,66,4,73,45,80,17]
### Your solution here
1C2. Write code to calculate and print the maximum, minimum, sum, count, and average of items in data (4 marks)¶
Hint: for the mean, you will need to combine the sum and the count
Sample output¶
The max is: 97
The min is: 4
The sum is: 1507
The count is: 30
The mean is: 50.233333333333334
### Your solution here
print('The max is: {0}'.format(<YOUR_CODE_HERE>)
print('The min is: {0}'.format(<YOUR_CODE_HERE>)
print('The sum is: {0}'.format(<YOUR_CODE_HERE>)
print('The count is: {0}'.format(<YOUR_CODE_HERE>)
print('The mean is: {0}'.format(<YOUR_CODE_HERE>)
1D3. (Optional) Using list comprehension (NOT for loops), print out the numbers within the specified upper and lower bounds (inclusive) of 12 and 80 (0 marks).¶
Sample output:¶
[53, 63, 40, 48, 53, 38, 63, 13, 15, 66, 57, 79, 42, 25, 66, 73, 45, 80, 17]
### Your solution here
Part 2: Working with data using pandas (12 marks)¶
In this part of the lab, we will practice loading in a sample data set using pandas, and doing some basic operations.
2A1. Load in the data (4 marks)¶
Here is the URL of the pokemon dataset inside the data folder.
Your task is to use the pandas read_csv() function to read this dataset, assign it to a dataframe called df, and then print its head also known as the first 5 lines of the dataframe.
Hint: don’t forget to first import pandas as pd to use read_csv and other pandas function.
### Your solution here
2A2. How many total pokemon are there in the dataset? (2 mark)¶
Make sure to use the dataframe.count() function to print the total number of entries in each column of the dataframe before you answer!
### Your solution here
2A3. Create a new dataframe df2 that only includes the Pokemon from the first generation. (2 marks)¶
Hint: Remember that you can subset dataframes using the [] syntax. More on this here
### Your solution here
2A4. Print ONLY the mean HP, Attack, Defense, and Speed of all pokemon in the first generation using pandas functions (4 marks)¶
### Your solution here
Part 3 - Dictionaries, Lists and data manapulation (10 marks)¶
In this part we explore another fundamental data structure in python, called Dictionaries.
3A. Create a dictionary that has 3 keys: name, age and salary, and enter in the following dummy information. (2 marks)¶
Sample output¶
{‘name’: ‘Tim Cook’, ‘age’: 59, ‘salary’: 3000000.0}
### Your solution here
### Your solution here
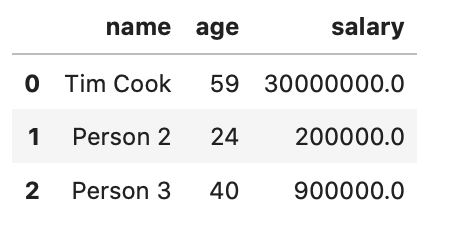
3B. Create a second dictionary, this time with at least 5 different names, ages, and salaries. (2 marks)¶
Hint: There should only be three keys, and the values should be a list.
Sample Output¶
{‘name’: [‘Tim Cook’, ‘Person 2’, ‘Person 3’], ‘age’: [59, 24, 40], ‘salary’: [30000000.0, 200000.0, 900000.0]}
### Your solution here
3C. Create a pandas dataframe using the dictionary you created above (2 marks)¶
Hint: Use the pd.DataFrame.from_dict() method
Part 4 - More dictionary practice (4 marks - Bonus)¶
(Bonus) (3 marks) Create a Python program that takes a string text and calculates the frequency of each letter. Data set (copy as string into Python code)
text = “””Elephants are mammals of the family Elephantidae and the largest existing land animals. Three species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. Elephantidae is the only surviving family of the order Proboscidea; extinct members include the mastodons. The family Elephantidae also contains several now-extinct groups, including the mammoths and straight-tusked elephants. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears, and convex or level backs. Distinctive features of all elephants include a long trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, massive legs, and tough but sensitive skin. The trunk, also called a proboscis, is used for breathing, bringing food and water to the mouth, and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. The pillar-like legs carry their great weight. Elephants are scattered throughout sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia and are found in different habitats, including savannahs, forests, deserts, and marshes. They are herbivorous, and they stay near water when it is accessible. They are considered to be keystone species, due to their impact on their environments.[1] Other animals tend to keep their distance from elephants; the exception is their predators such as lions, tigers, hyenas, and wild dogs, which usually target only young elephants (calves). Elephants have a fission–fusion society, in which multiple family groups come together to socialise. Females (cows) tend to live in family groups, which can consist of one female with her calves or several related females with offspring. The groups, which do not include bulls, are led by the (usually) oldest cow, known as the matriarch.”””
Hint: There are many ways to do this, the most “elegant” way uses a mixture of sets, and the Counter modules from collections
Sample output:¶
‘ ‘: Count of 293 and Percentage of 15.2%
‘(‘: Count of 3 and Percentage of 0.2%
‘)’: Count of 3 and Percentage of 0.2%
‘,’: Count of 32 and Percentage of 1.7%
‘-‘: Count of 4 and Percentage of 0.2%
‘.’: Count of 17 and Percentage of 0.9%
‘1’: Count of 1 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘:’: Count of 1 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘;’: Count of 2 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘A’: Count of 8 and Percentage of 0.4%
‘D’: Count of 1 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘E’: Count of 6 and Percentage of 0.3%
‘F’: Count of 1 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘O’: Count of 1 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘P’: Count of 1 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘S’: Count of 3 and Percentage of 0.2%
‘T’: Count of 9 and Percentage of 0.5%
‘[‘: Count of 1 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘]’: Count of 1 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘a’: Count of 147 and Percentage of 7.6%
‘b’: Count of 20 and Percentage of 1.0%
‘c’: Count of 55 and Percentage of 2.8%
‘d’: Count of 53 and Percentage of 2.7%
‘e’: Count of 189 and Percentage of 9.8%
‘f’: Count of 32 and Percentage of 1.7%
‘g’: Count of 37 and Percentage of 1.9%
‘h’: Count of 84 and Percentage of 4.4%
‘i’: Count of 109 and Percentage of 5.6%
‘j’: Count of 2 and Percentage of 0.1%
‘k’: Count of 12 and Percentage of 0.6%
‘l’: Count of 80 and Percentage of 4.1%
‘m’: Count of 35 and Percentage of 1.8%
‘n’: Count of 114 and Percentage of 5.9%
‘o’: Count of 87 and Percentage of 4.5%
‘p’: Count of 34 and Percentage of 1.8%
‘r’: Count of 92 and Percentage of 4.8%
‘s’: Count of 131 and Percentage of 6.8%
‘t’: Count of 120 and Percentage of 6.2%
‘u’: Count of 41 and Percentage of 2.1%
‘v’: Count of 22 and Percentage of 1.1%
‘w’: Count of 19 and Percentage of 1.0%
‘x’: Count of 5 and Percentage of 0.3%
‘y’: Count of 21 and Percentage of 1.1%
‘–’: Count of 1 and Percentage of 0.1%
text = """Elephants are mammals of the family Elephantidae and the largest existing land animals. Three species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. Elephantidae is the only surviving family of the order Proboscidea; extinct members include the mastodons. The family Elephantidae also contains several now-extinct groups, including the mammoths and straight-tusked elephants. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears, and convex or level backs. Distinctive features of all elephants include a long trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, massive legs, and tough but sensitive skin. The trunk, also called a proboscis, is used for breathing, bringing food and water to the mouth, and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. The pillar-like legs carry their great weight. Elephants are scattered throughout sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia and are found in different habitats, including savannahs, forests, deserts, and marshes. They are herbivorous, and they stay near water when it is accessible. They are considered to be keystone species, due to their impact on their environments.[1] Other animals tend to keep their distance from elephants; the exception is their predators such as lions, tigers, hyenas, and wild dogs, which usually target only young elephants (calves). Elephants have a fission–fusion society, in which multiple family groups come together to socialise. Females (cows) tend to live in family groups, which can consist of one female with her calves or several related females with offspring. The groups, which do not include bulls, are led by the (usually) oldest cow, known as the matriarch."""
### Your solution here